NASA’s GRAIL Mission Puts a New Face on the Moon
Nov. 7, 2013. Scientists using data from the lunar-orbiting twins of NASA’s Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission are gaining new insight into how the face of the moon received its rugged good looks. A report on the asymmetric distribution of lunar impact basins is published in this week’s edition of the journal Science.
“Since time immemorial, humanity has looked up and wondered what made the man in the Moon,” said Maria Zuber, GRAIL principal investigator from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge. “We know the dark splotches are large, lava-filled, impact basins that were created by asteroid impacts about four billion years ago. GRAIL data indicate that both the near side and the far side of the Moon were bombarded by similarly large impactors, but they reacted to them much differently.”
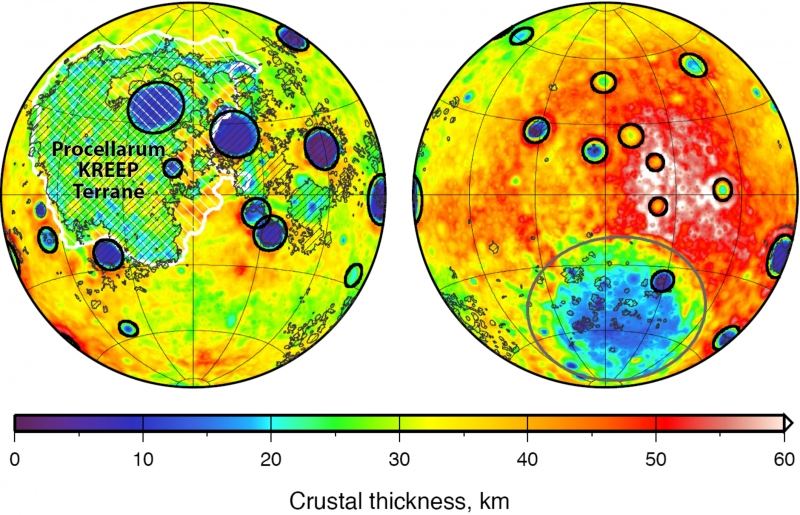
Global map of crustal thickness of the Moon derived from gravity data obtained by NASA’s GRAIL spacecraft. The lunar near side is represented on the left hemisphere, and the far side is represented in the right hemisphere. In the left hemisphere, outlined in white, is the Procellarum KREEP Terrane, a large province on the near side of the Moon that contains high abundances of potassium, rare-earth elements and phosphorus. Excluding the Aitken basin at the south pole (the gray circle on the lower half of the far side hemisphere), there are 12 impact basins with crustal thinning that have diameters greater than 200 kilometers on each hemisphere. Those are marked with black circles. The image is presented in two hemispherical Lambert azimuthal equal-area projections centered over the near side (left), and far side (right) hemispheres. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/S. Miljkovic. |
Understanding lunar impact basins has been hampered by the simple fact that there is a lack of consensus on their size. Most of the largest impact basins on the near side of the Moon (the moon’s face) have been filled with lava flows, which hide important clues about the shape of the land that could be used for determining their dimensions. The GRAIL mission measured the internal structure of the Moon in unprecedented detail for nine months in 2012. With the data, GRAIL scientists have redefined the sizes of massive impact basins on the Moon.
Maps of crustal thickness generated by GRAIL revealed more large impact basins on the near-side hemisphere of the Moon than on the far side. How could this be if both hemispheres were, as widely believed, on the receiving end of the same number of impacts?
Scientists have long known that the temperatures of the near-side hemisphere of the Moon were higher than those on the far side: the abundances of the heat producing elements uranium and thorium are higher on the near side than the far side, and as a consequence, the vast majority of volcanic eruptions occurred on the Moon’s near-side hemisphere.
“Impact simulations indicate that impacts into a hot, thin crust representative of the early Moon’s near-side hemisphere would have produced basins with as much as twice the diameter as similar impacts into cooler crust, which is indicative of early conditions on the moon’s far-side hemisphere,” notes lead author Katarina Miljkovic of the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris.
The new GRAIL research is also helping redefine the concept of the late heavy bombardment, a proposed spike in the rate of crater creation by impacts about 4 billion years ago. The late heavy bombardment is based largely on the ages of large near-side impact basins that are either within, or adjacent to the dark, lava-filled basins, or lunar maria, named Oceanus Procellarum and Mare Imbrium. However, the special composition of the material on and below the surface of the near side implies that the temperatures beneath this region were not representative of the Moon as a whole at the time of the late heavy bombardment. The difference in the temperature profiles would have caused scientists to overestimate the magnitude of the basin-forming impact bombardment. Work by GRAIL scientists supports the hypothesis that the size distribution of impact basins on the far-side hemisphere of the moon is a more accurate indicator of the impact history of the inner solar system than those on the near side.
Launched as GRAIL A and GRAIL B in September 2011, the probes, renamed Ebb and Flow by schoolchildren in Montana, operated in a nearly circular orbit near the poles of the Moon at an altitude of about 55 kilometers until their mission ended in December 2012. The distance between the twin probes changed slightly as they flew over areas of greater and lesser gravity caused by visible features, such as mountains and craters, and by masses hidden beneath the lunar surface.
JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, Calif. managed GRAIL for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The mission was part of the Discovery Program managed at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, in Greenbelt, Md., manages the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. Operations of the spacecraft’s laser altimeter, which provided supporting data used in this investigation, is led by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge. Lockheed Martin Space Systems in Denver built GRAIL.
For more information about the mission, visit:
http:grail.nasa.gov or http://www.nasa.gov/grail .
DC Agle 818-393-9011
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
agle@jpl.nasa.gov
Dwayne Brown 202-358-1726
NASA Headquarters, Washington
Dwayne.c.brown@nasa.gov
Sarah McDonnell 617-253-8923
Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge
s_mcd@mit.edu
