E2: Impact of black holes on their environment
Following the recommendations of the 2013 Scientific Committee, the project was stopped.
-
From the micro-quasars of the dark ages to the super-massive black holes of the local universe
SCIENTIFIC PROGRAM1. Scientific context
Black holes are certainly between the most fundamental objects of our universe as they can probe and possibly link some of the fundamental theories in physics. However today they can be observed and experimentally studied only in an astrophysical context through the specific effects they induce on matter and radiation that are sufficiently close to their horizon. The aim of the proposed project is to investigate the properties, the evolution history and the cosmic role of black holes through the study of the impact they have on their environment at different scales and at different cosmic times. In order to tackle this ambitious program we propose to focus the research project on the following four distinct topics.

Artist concept of matter swirling around a black hole (NASA/Dana Berry/SkyWorks Digital)
a. Stellar mass black holes in the re-ionization eraThe so called “dark ages” of the universe began about 400.000 years after the Big Bang as matter cooled down and space became filled with neutral hydrogen for hundreds of millions years. How most of the matter in the universe became again ionized (re-ionized) and was re-heated over large volumes of space in less than a billon year is a question of topical interest in cosmology. Observational evidence exists for extensive star formation up to z ~ 8-10. The detection of the explosion of a massive star at z ~ 8.2 provides further evidence for the collapse of massive stars into black holes at these early epochs, producing a large population of high mass black hole x-ray binaries. We propose that the thermal (UV and soft x-rays) and non-thermal (hard x-rays, winds and jets) emission from this large population of stellar black hole high mass binaries heated the intergalactic medium over large volumes of space during the re-ionization era of the universe. Feedback from accreting stellar black holes at that epoch may have direct implications for models on the minimum mass required for the formation of dwarf galaxies and for existing and future atomic hydrogen radio surveys of HI in the early universe. We propose to study this feedback theoretically, and through intensive simulations.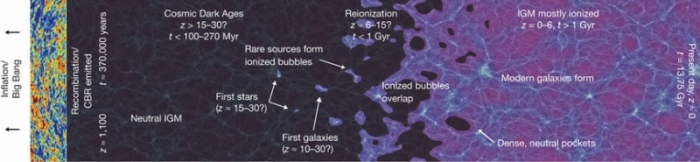
Reionization era (from Robertson, B. E., et al., 2010, Nature, 468, 49)
b. The feedback of super-massive black holes on the galaxy bulges in AGNIt is well known that all galaxies show a tight correlation between the mass of their central super-massive black hole and the velocity dispersion of the stars in their bulge. This proves that there is some form of feedback between the black hole growth and the galaxy evolution. The nature of this feedback however is not known and remains one of the crucial mysteries of modern astronomy. We intend to investigate the nature of the feedback, most probably relativistic particle ejectionsand/or plasma outflows, with the study of a selected sample of active galactic nuclei to be performed with the data of present high energy space telescopes as XMM, Integral, Fermi and Hess and future facilities like Astro-H.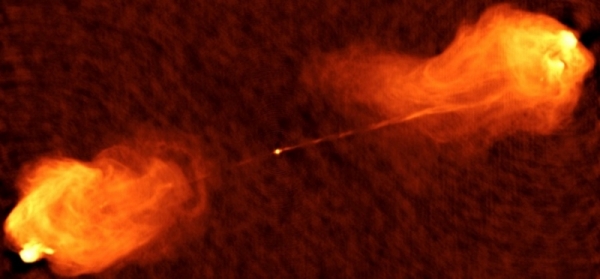
Radio image of the Cygnus A active galactic nuclei (NRAO)
c. Impact on the environment of the past intense activity of the super-massive black hole at the galactic centerThe super-massive black hole at the center of our own Galaxy, associated to the source Sgr A*, is extremely quiet at the present times, and characterizes the quiescent phase of the black holes in the galactic nuclei of the local universe. However our recent X-ray and gamma-ray observations (with XMM and Integral) of the molecular clouds of the central zone have shown that Sgr A* underwent a powerful outburst few hundred years ago during which its X-ray luminosity increased by a factor of over one million. This phase of activity lasted for about 400 years and left its imprint in the molecular clouds of the region that reflect this radiation towards us with a delay that depends on their spatial distribution around the center. The molecular cloud emission variations allow us to explore both the behavior of the black hole in the past and the very complex matter distribution in the central region. Such an active phase of the central black hole must have also induced variations in its complex interstellar environment. Evidences for such impact on the chemistry of clouds have been already found with observations of radio molecular lines such as those of SiO and HCO. We propose to open a new field of investigation in our laboratories, to be carried out in parallel to our large program of X-ray and gamma-ray observations of the Galactic Center, in order to study ionization, heating and chemistry changes of the surrounding interstellar matter (ISM) induced by the past activity of the supermassive black hole. The outcome of this study will also allow a better understanding of conditions in the central galactic region, important for the cosmic ray particle propagation and interaction.
Combined radio and infrared images of the Central Molecular Zone in the Center of our Galaxy
d. Impact of jets and outflows from stellar mass black holes on their environment and interaction between compact object and companion star in binary systemsThis part of the program will explore the impact of galactic stellar mass black holes in X-ray binary systems on both the surrounding interstellar matter and on the companion star of the system. Not only the relativistic jets have an influence on the environment of the microquasars, but also the compact object itself has an influence on its companion star, gravitationally bound in the binary system. This program will include:1. Study of the nature and characteristics of the compact object of the binary system, which are modified by accretion and ejection of matter.2. Study of the companion star properties that are modified by the compact object: mass loss, angular momentum, composition, rotation, the structure of the stellar wind, etc…3. Study of the impact of microquasars on the ISM through the intense radiation, the relativistic jets or other outflows (e.g. bubbles of shocked ISM by relativistic ejections).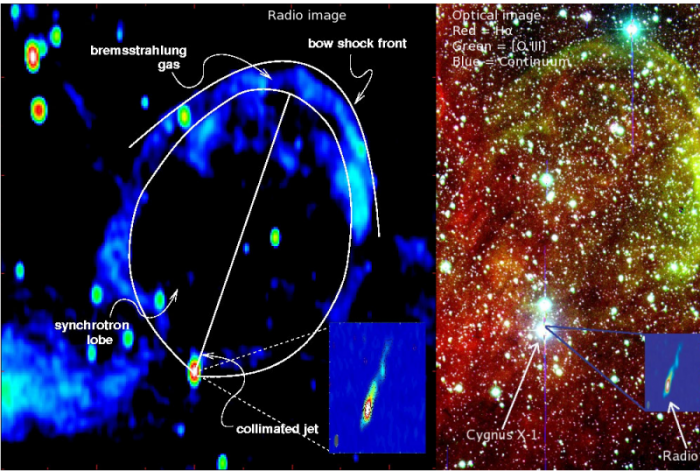
Features around the black hole high mass X-ray binary Cyg X-1 (from Gallo et al. 2005, Russel et al. 2007)
2. ProgramWe propose to carry out this collaborative work with the contribution of world-wide known experts who will be invited for long period stays (typically one year) and of young scientists at post-doc level that will be also selected for the complementary expertise they can provide to our present teams (simulations, ISM chemistry, radio data analysis). These experts and scientists will provide part of the initial expertise lacking in our laboratories, to develop the study of the re-ionization era, impact of extragalactic black holes and the Galactic Center environment. The first year will be dedicated to a theoretical, detailed description of the problems. Deeper investigations will be made possible then by extended simulations of the physical processes. A continuous exchange between theory, simulations and available data will lead to a more detailed view of the impact of black holes on their environment. Precise observable quantities will be predicted, in order to test our study results with the present and next generation telescopes. This project will allow us to prepare the future radio, infrared and X-ray observations which our laboratories will carry out in the future with the next generation of telescopes.This project will open new area of interdisciplinary studies in high energy astrophysics but will build up on the strong expertise that APC and AIM teams have in the field of microquasars, jets, AGNs and galactic center physics and on their already existing research programs. This project will optimize the scientific return of present and future X and gamma ray missions in which the two laboratories are involved.Two years of exploratory study supported by visiting senior scientists will allow focusing the project on two of the items mentioned above, that will then be covered with 3 years of intense work with simulations and data analysis supported by the post-doc positions. -
Position, Topic Name Laboratory Grade, employer Leader, [C] Goldwurm Andrea APC Research Director, CEA Co-leader, [A] Mirabel, Felix AIM Research Director, CEA Member, [B] Beckmann Volker< PC Post-Doc CNRS Member, [D] Chaty Sylvain AIM Professor, Univ. Paris Diderot Member, [C] Clavel Maica APC PhD Student Member, [D] Coleiro Alexis AIM PhD Student Member, [B] De Jong Sandra APC PhD Student Member, [A] Laurent Philippe APC Research Director, CEA Member, [B,C] Soldi Simona AIM, APC Post-Doc CNES, CNRS Member, [C] Terrier Regis APC Researcher CR1, CNRS/IN2P3 Member, web-page man. [C] Trap Guillaume APC Scientist, Palais de la Decouverte, Scient. Collaborator APC and CEA -
Summary of Reasearch Activities and Observations 2011-2013
(in bold the activities directly financed through the E2 project)
A] Stellar-Mass Black Holes in the re-ionization era (FM, PL)
International Collaborations:
- Dr. Mark Dijkstra, MPA-Garching, Germany
- Prof. Lev Titarchuk, Univ. of Ferrara, Italy
- Dr. Leonardo Pellizza, IAFE, Buenos Aires, Argentina
Visiting Scientist Programs:
- Mark Dijkstra, MPA-Garching, Germany, visiting scientist at AIM & APC in April 2013
- Lev Titarchuk, Univ. of Ferrara, Italy, visiting scientist at APC & AIM in April 2013
- Vanesa Douna, IAFE Buenos Aires, Argentina, visiting PhD student at AIM & APC, 2 -16 Sep 2013
- [F. Mirabel, visit of IAFE Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1 month, April-May 2014]
B] SuperMassive Black Holes in AGN (VB, SS, SDJ)
Formation activities: Master trainings, PhDs, Thesis and Post-doctoral positions
- March-June 2011: Master 2 research traineeship on AGN emission processes of NGC 4945 in the X-rays and gamma-rays by M.-L. Menzel (supervisor VB)
- May-July 2012: Master 1 research traineeships on X-ray emission from the radio galaxies M87 and Cen A by Dounia Saez and Pierre Li Cavoli (supervisor VB)
- since Oct 2010: PhD thesis of S. de Jong on “Accretion Processes in Active Galactic Nuclei at high energies” (supervisor: VB)
Accepted Observation Proposals and Programs:
- INTEGRAL and SWIFT simultaneous observations of NGC 7172 performed in 2011 (PI: SS)
- INTEGRAL and SWIFT simultaneous observations of NGC 5506 performed in 2012 (PI: SS)
- SWIFT and INTEGRAL follow-up of non-blazar Fermi AGN performed in 2012 (PI: SDJ)
- INTEGRAL observations of M87 performed in 2011 and 2012 (PI: VB)
- INTEGRAL and XMM-Newton simultaneous observations of NGC 2992 approved in 2011 (PI: VB) and then performed in 2013
- INTEGRAL proposal to observe NGC 2110 submitted (PI VB) and approved in 2013
Workshops, Conferences, Collaboration Programs:
- “The X-ray Universe 2011” conference in Berlin (June 2011): contributed talks (VB, SS) and poster (SDJ)
- “The Physics of Astronomical Transients” conference in Aspen (USA, January 2012): contributed talks (SS, VB)
- Fermi summer school in Lewes (USA, May 2012): contributed talk (SDJ)
- COSPAR 2012, Mysore (India, July 2012), VB as main scientific organizer of escientific event (invited talk and 2 posters by VB)
- 9th INTEGRAL Workshop (Paris, October 2012): contributed talk by SS and VB, posters by SS, VB, SDJ
- Organisation of a session on “Outflows and Accretion from White Dwarfs to Supermassive Black Holes” (VB deputy scientific organiser) at the next COSPAR Assembly, 2014 in Moscow
- Spring school on Cosmic Accelerators, Cargèse, France, 29 April-8 May 2013, with contributed talk (SdJ) and lecture (VB)
- Conference The restless nature of AGNs: variability as a probe of the central engine, Naples, Italy, 20-23 May 2013, contributed talk by SS
- Participation to the INTEGRAL Workshop, Rome, 15-18/10/2013, invited talk by VB
International Collaborations:
- C. Shrader, NASA/GSFC, Greenbelt, US
- P. Lubinski, Torun, Poland
- N. Gehrels, NASA/GSFC, Greenbelt, US
- C. Ricci, ISDC, Geneva, Switzerland and then Kyoto Univ., Japan
- A. Tramacere, ISDC, Geneve, CH
- J. Tueller, NASA/GSFC, Greenbelt, US
- J. Kennea, Penn State University, Philadelphia, US
Visiting Scientist Programs:
- Chris Shrader, visiting scientist at APC in October 2011
C] The Galactic Center SuperMassive Black Hole (AG, RT, MC, SS, GT)
Formation activities: Master training, PhD Thesis and Post-doctoral positions
- 2011: Master 1 reasearch traineeship on Limits on the past activity of the GC SMBH on the basis of the INTEGRAL data by A. Pottier (supervisor RT)
- March-June 2011: Master 2 research traineeship (Doctoral School: A&A) on Search for past activities of close SMBH in external galaxies by M. Clavel (supervisor RT)
- Sep 2011: Thesis defense (Doctoral School: NPAC) of G. Trap on Galactic Center High Energy emission (supervisor AG)
- since Oct 2011: PhD thesis on the Galactic Center Black Hole of M. Clavel (supervisors: AG and RT)
- since Dec 2012: CNES fellowship (2 yrs) for S. Soldi to work at APC on the data of the 2012 XMM Large Project survey of the Galactic Center.
Observation Proposals and Programs:
- Chandra Obs. of Molecular Clouds around Sgr A complex performed in July 2011 (PI: RT)
- XMM / VLT Observations of Sgr A* in March 2012 (PI: AG), participation to a new large multi-wavelength campaign on Sgr A* (visiting observer at Paranal: MC)
- A Large Project (700 ks) proposal for obs. with XMM of the GC region for the XMM AO11 call submitted in Oct 2011 (PI: RT) and approved
- LP XMM Observations of the GC region (PI: RT) performed in October 2012
- Two Proposals (1 survey, 1 ToO) for XMM Obs. in 2013 of the cloud G2 approaching Sgr A* submitted for AO12 in Oct. 2012 and approved (PI: Ponti)
- Proposal for a 100 ks observation of Sgr C with Chandra (PI: SS) submitted in March 2013 and approved for Chandra cycle 15
- Proposal for sub-mm Carma observations of Sgr A molecular complex, submitted May 2013 (PI: MC) approved October 2013
- Proposal for XMM observations of Sgr B2 complex submitted in October 2013 (PI: RT)
Workshops, Conferences, Collaboration Programs:
- Proposal for an ISSI international team submitted in 2011 (PI: AG) and approved
- GC ISM Heidelberg Meeting (October 2011): 2 invited talks (AG, RT), 1 poster (MC)
- Ginzburg Conference on theoretical physics (Moscow, May 2012), invited talk on Activity of the GC SMBH by AG
- First ISSI IT meeting on the Galactic Center held in May 2012, see the IT ISSI Web pages at http://www.issibern.ch/teams/galacticbh/
- 2012 SF2A meeting, Nice, June 2012, contr. talk by MC (financed: Ecole Doctorale, PNHE)
- COSPAR 2012, Mysore, India, July 2012, scientific event, invited talk by AG
- 9th INTEGRAL Workshop, Paris, October 2012, solicited talk by RT, contributed talk by MC
- Organization of a session on the Galactic Center Supermassive Black Hole at the next COSPAR Assembly, 2014 in Moscow (AG main scientific organiser)
- Proposal to the Ulysses call for reasearch visits program with Ireland, for a collaboration with M. Chernyakova’s group in Dublin to develop together a simulation code of reflection processes in the GC region, submitted in Sep 2012 (PI: AG, M. Chernyakova), approved
- Lorentz Center Workshop: A New View of Accretion onto our Galactic Center Supermassive Black Hole, Leiden, The Neetherlands, January 2013, talk by AG
- Second ISSI IT meeting on the Galactic Center held in May 2013, see the IT ISSI Web pages
- Spring school on Cosmic Accelerators, Cargèse, France, 29 April-8 May 2013, (MC)
- IAU symposium 303 The Galactic Center: Feeding and Feedback in a Normal Galactic Nucleus, Santa Fe, US, October 2013, with 1 contributed talk by MC, 3 posters by SS and GT
- Participation to the INTEGRAL Workshop 2013, Rome, 15-18/10/2013, invited talk by AG
International Collaborations:
- Prof. Fulvio Melia, Arizona Un.,Tucson, US
- Dr. Gabriel Ponti, Southampton Un., UK and then MPE, Garching, Germany
- Prof. Mark Morris, UCLA, Los Angeles, US
- Dr. Maria Chernyakova, Dublin, Ireland
- Dr. Maurizio Falanga, ISSI, Bern, CH
- Prof. Vladimir Dogiel, Lebedev Institute, Moscow, Russia
- Participation to the Chandra XVP on Sgr A* Large International collaboration (MC, AG)
Visiting Scientist Programs:
- Fulvio Melia, visiting scientist at APC from 11/06 to 29/06/ 2012
- Maïca Clavel, visiting PhD student at MPE Garching from 10/04 to 20/04 2013
- Maïca Clavel, visiting PhD student at MPE Garching from 15/06 to 30/06 2013 (COST BH in the Universe)
- Mark Morris, visiting scientist at APC from 2/9 to 18/9/ 2013
- Michael Walls, visiting PhD student at APC, 2-7June 2013 (Ulysses Program)
- Masha Chernyackova and M. Walls, visiting scientist and PhD student at APC, September 2013 (Ulysses Program)
- Visit of Dublin University (DCU), Ireland by R. Terrier, M. Clavel and A. Goldwurm 18 – 22 Nov 2013 (Ulysses Program)
- Maïca Clavel, visiting PhD student at MPE Garching from 2/12 to 4/12 2013
- Fulvio Melia, visiting scientist at APC, 8 – 20 Dec 2013
D] Galactic Stellar-Mass Black Hole Binaries (SC, AC)
Formation activities: Master training, PhD Thesis and Post-doctoral positions:
- Oct 2010 – Oct 2013: PhD thesis on Nature, formation and evolution of High Mass X-ray Binaries by Alexis Coleiro (supervisor: SC)
Workshops, Conferences, Collaboration Programs:
- Variable Galactic Gamma-Ray Sources, Barcelona, April 16-18, 2013 (invited review of SC)
- XXXVIIIth Rencontres de Moriond Astrophysics “Very High Energy Phenomena in the Universe”, La Thuile, 03/2013 (invited review of SC)
- IXth INTEGRAL Workshop: Paris, 10/2012 (contributed talks of SC and AC)
- 39th COSPAR Scientific Assembly 2012, Event 1.4 “Unveiling the properties of Supergiant Fast X-ray Transients”, Mysore, India, 14-22 July 2012, (invited review of SC)
International Collaborations:
- Dr. Thomas Tauris (Bonn University, Max Planck fur Radio-Astronomie, Argelander Inst.).
- Dr. John A. Tomsick (Space Sciences Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley)
- Prof. Gustavo E. Romero (University of La Plata, Argentina)
Visiting Scientist Programs:
- Prof. Gustavo E. Romero, visiting scientist at AIM, Nov-Dec 2013 (PRESSPC)
- [ Dr. Thomas Tauris, visiting scientist at AIM, planned early 2014 ]
-
PUBLICATIONS mid-2011 – 2013 (in bold publications directly supported by E2)
Books, Monographs, Thesis:
- Beckmann, V. & Shrader, C.R.; Active Galactic Nuclei, 2012, ISBN-13: 978-3527410781. 350 pages. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, 2012
- Ponti, G., Morris, M., Terrier, R., Goldwurm, A.; Traces of past activity in the Galactic Centre. 2013, In Advances in Solid State Physics, Vol. 34, “Cosmic Rays in Star-Forming Environments”, eds. Olaf Reimer and Diego F. Torres, 331 (arXiv:1210.3034)
- Sandra De Jong, Accretion processes of radio galaxies at high energies, University: Observatoire de Paris, Ecole Doctorale Astronomie & Astrophysique d’Ile-de-France, defended 29 October 2013 at FACe/APC Paris Diderot
- Alexis Coleiro, Etude Multilongueur d’onde d’étoiles binaires accrétantes de grande masse, University Paris Diderot, Ecole Doctorale Astronomie & Astrophysique d’Ile-de-France, defended 25 September 2013 at SAp/IRFU/CEA Saclay
Refereed Papers:
- Beckmann, V., et al.; The hard X-ray emission of Centaurus A, 2011, A&A 531, 70
- Bower, G., …, Clavel, M. Goldwurm, A., …, Detection of Variability in the Size of Sagittarius A*, 2013, ApJL, submit.
- Chaty, S., Dubus, G., Raichoor, A.; Near-infrared jet emission in the microquasar XTE J1550-564, 2011, A&A, 529, A3
- Chaty, S., Rahoui, F., Mid-infrared spectroscopy revealing the surroundings of the obscured High Mass X-ray binary IGR J16318-4848, 2012, ApJ, 751, 150
- Chaty, S., Muñoz Arjonilla, A.J., Dubus, G., Infrared study of H1743-322 in outburst: a radio-quiet microquasar, 2013, A&A, submit.
- Clavel, M., Terrier, R., Goldwurm, A., Morris, M., Ponti, G., Soldi, S., Trap, G., Echoes of multiple outbursts of Sagittarius A* revealed by Chandra, 2013, A&A, 558, 32 (arXiv:1307.3954)
- Coleiro, A., Chaty, S., Distribution of High Mass X-ray Binaries in the Milky Way, 2013, ApJ, 764, 185
- Coleiro, A., Chaty, S., et al., Infrared identification of high-mass X-ray binaries discovered by INTEGRAL, 2013, A&A, in press (arXiv:1013.0451)
- Curran, P.A., Chaty, S., Zurita Heras, J.A.; Disentangling the nIR/optical emission of black hole XTE J1650-500 during outburst, 2012, A&A, 547, 41
- Curran, P.A., Chaty, S., Near-infrared and optical observations of the failed outbursts of black hole XTE J1550-564, 2013, A&A, 557, 45
- de Jong, S., Beckmann, V., Mattana, F.; The nature of the multi-wavelength emission of 3C 111, 2012, A&A 545, 90
- Dodds-Eden, K., .., Goldwurm, A., .., Trap, G., et al.; The Two States of Sgr A* in the Near-infrared: Bright Episodic Flares on Top of Low-level Continuous Variability, 2011, ApJ, 728, 37
- Dogiel, V. A., Chernyshov, D. O., Tatischeff, V., Cheng, K.-S., Terrier, R.; The Origin of the 6.4 keV Line Emission and H2 Ionization in the Diffuse Molecular Gas of the Galactic Center Region, 2013, ApJ, 771, L43
- Melia, F., Falanga, M., Goldwurm, A.; Polarimetric imaging of Sgr A* in its flaring state, 2012, MNRAS, 419, 2489
- Mirabel, I. F., Dijkstra, M., Laurent, P., Loeb, A., Pritchard, J. R.; Stellar black holes at the dawn of the universe, 2011, A&A 528, 149
- Soldi, S., Beckmann, S., Baumgartner, W.H., Ponti, G., Shrader, C.R., Lubinski, P., Krimm, H.A., Mattana, F., Tueller, J., Long-term variability of AGN at hard X-rays, 2013, A&A, in press (arXiv:1311.4164)
- Trap, G., Goldwurm, A., et al.; Concurrent X-ray, near-infrared, sub-millimeter, and GeV gamma-ray observations of Sagittarius A*, 2011, A&A, 528, 140
- Zurita Heras, J. A., Chaty, S., Cadolle-Bel, M., Prat, L.; Evidence of an irradiated accrétion disc in XTE J1818-245, 2011, MNRAS, 413, 235
Conference Proceedings:
- Beckmann, V., Jean, P., Lubiński, P., Soldi, S., Terrier, R.; The dominant emission process of the X-ray spectrum of Cen A, 2011, Proc. of the Conf. “The X-ray Universe”, Berlin 2011, id 34
- Beckmann, V., De Jong, S., Mattana, F., Saez, D., Soldi, S.; Gamma-ay emitting radio galaxies at hard X-rays: Seyfert core or jet emission ? ; 2013, PoS INTEGRAL 2012, id 058
- Beckmann, V., Shrader, C.; The AGN phenomenon: open issues; 2013, PoS INTEGRAL 2012, id69
- Clavel, M., Terrier, R., Goldwurm, A., Morris, M., Ponti, G., Soldi, S., Trap, G.; Chandra observations of the X-ray emission from Molecular Clouds at the Galactic Center related to Sgr A* past activity; 2013, PoS INTEGRAL 2012, id 106
- Clavel, M., Terrier, R., Goldwurm, A., Morris, M., Ponti, G., Soldi, S., Trap, G.; The reflection of two past outbursts of Sagittarius A* observed by Chandra during the last decade, 2013, Conf. Proc of IAU 303 Symp. “The Galactic Center: Feeding and Feedback in a Normal Galactic Nucleus”, 30/9-4/10/2013, Santa Fe, NM, USA, submit.
- Coleiro, A., Chaty, S., Zurita Heras, J.A., Rahoui, F., Tomsick, J.A., Identification of 12 High Mass X-Ray Binaries detected by INTEGRAL through NIR photometry and spectroscopy2013, PoS INTEGRAL 2012, id
- de Jong, S., Beckmann, V.; The non-thermal core of 3C 111, 2011, Proc. of the Conf. “The X-ray Universe”, Berlin 2011, id 309
- de Jong, S., Beckmann, V., Soldi, S., et al.; M87 in hard X-rays: an INTEGRAL view; 2013, PoS INTEGRAL 2012, id 070
- de Jong, S., Beckmann, V., Mattana, F.; The non-thermal core of 3C 111, 2012, Proceedings of Science, SISSA, PoS(Extremesky 2011) 076.
- Mirabel, I. F.; Stellar black holes: Cosmic history and feedback at the dawn of the universe, 2011, IAU Symp., 275, 3 (arXiv:1012.4944)
- Menzel, M.L., Beckmann, V., Mattana, F.; AGN emission processes of NGC 4945 in the X-rays and gamma-rays, 2012, Proceedings of Science, SISSA, PoS (Extremesky 2011) 075
- Soldi, S., et al.; AGN variability at hard X-rays, 2011, Proc. of the Conf. “The X-ray Universe”, Berlin 2011, id 154
- Soldi, S., et al.; High-energy emission from NGC 5506, the brightest hard X-ray Narrow Line Seyfert 1 galaxy, 2011, Proc. of the Conf. “NLS1 Galaxies and their place in the Universe”, Milan 2011
- Soldi, S., Baumgartner, W., Beckmann, V., et al.; AGN variability at hard X-rays; 2013, PoS INTEGRAL 2012, id 65
- Soldi, S., Clavel, M., Goldwurm, A., Morris, M., Ponti, G., Terrier, R., Trap, G.; An X-ray survey of the Central Molecular Zone: variability of the Fe Kalpha emission line, 2013, Conf. Proc of IAU 303 Symp. “The Galactic Center: Feeding and Feedback in a Normal Galactic Nucleus”, 30/9-4/10/2013, Santa Fe, NM, USA, submit.
- Soldi, S., Clavel, M., Goldwurm, A., Ponti, G., Terrier, R., Trap, G., Greiner, J., Prinz, T., Rau, A., Servillat, M.; A new Very Faint X-ray Transient in the Galactic centre, 2013, Conf. Proc of IAU 303 Symp. “The Galactic Center: Feeding and Feedback in a Normal Galactic Nucleus”, 30/9-4/10/2013, Santa Fe, NM, USA, submit.
- Trap, G., Ponti, G., Soldi, S., Clavel, G., Terrier M., Goldwurm, A., Thermonuclear bursts from AX J1745.6–‐2901, 2013, Conf. Proc of IAU 303 Symp. “The Galactic Center: Feeding and Feedback in a Normal Galactic Nucleus”, 30/9-4/10/2013, Santa Fe, NM, USA, in preparation
